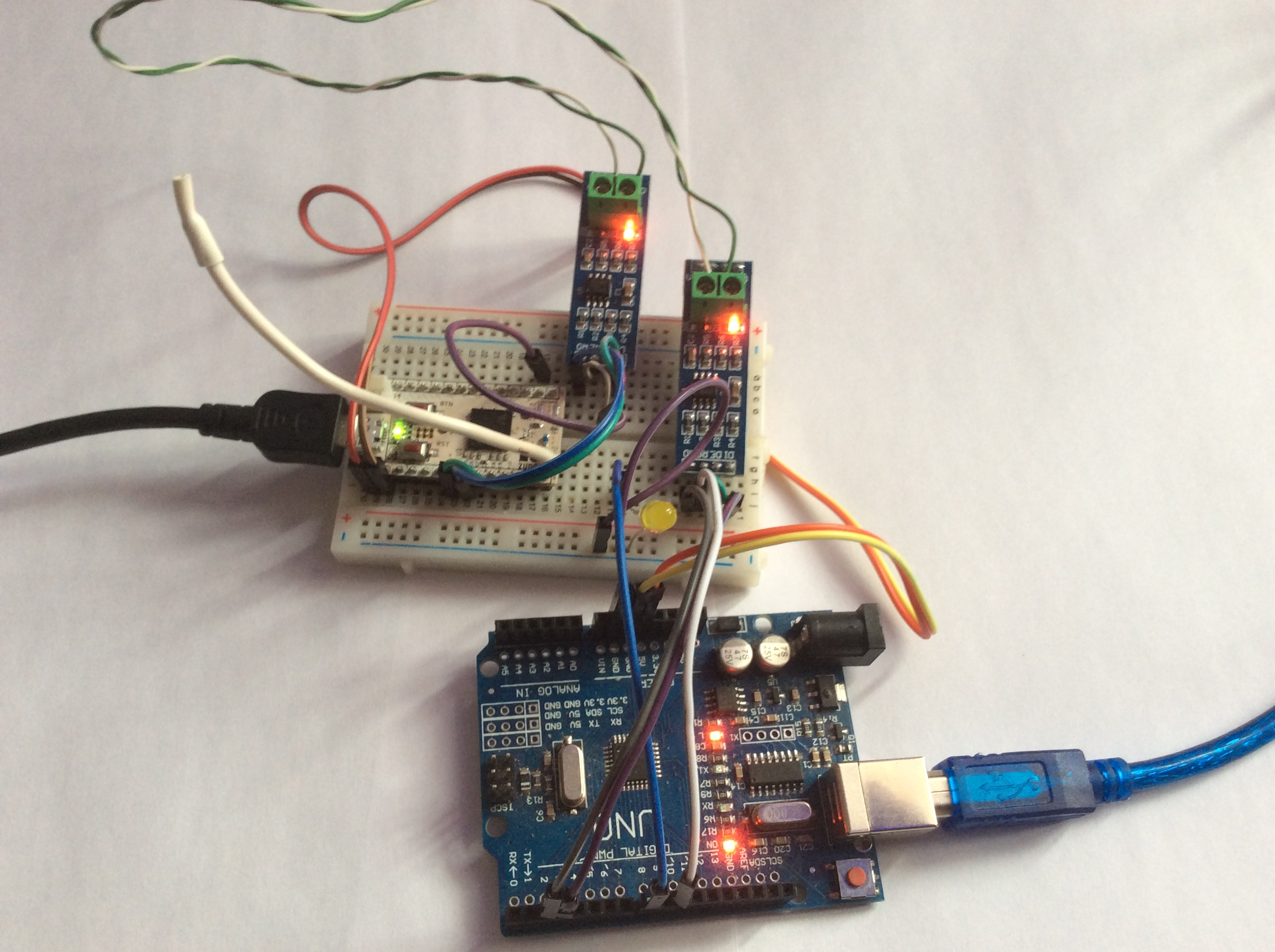
RS-485 bus based on MAX485 Chip
Example of RS-485 bus communications using MAX485 chip. Z-Uno Switch Binary channel state is sent via RS485 bus to a slave device based on Arduino Uno.Download Fritzing project
// demo sketch connecting Z-Uno to the RS485 network and sending commands to slave device (Arduino Uno) the status of the Switch Binary channel
// set up channel
ZUNO_SETUP_CHANNELS(
ZUNO_SWITCH_BINARY(getter, setter)
);
// pin for send/get rs485
int pin_direction_RX_TX = 10;
// address slave device arduino uno
int address = 1;
// status SWITCH BINARY
int statusswitch = 0;
//
unsigned long millisdelay = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin();
Serial0.begin(9600);
pinMode(pin_direction_RX_TX, OUTPUT);
// to get data RS485
digitalWrite(pin_direction_RX_TX, LOW);
}
void loop() {
// every 30 second
if(millis() - millisdelay > 30000) {
// send data to channel
zunoSendReport(1);
millisdelay = millis();
}
// get data from slave device (Arduino Uno)
if(Serial0.available() > 0) {
char c = Serial0.read();
Serial.print(c,HEX);
}
}
// getter function
int getter() {
return statusswitch;
}
// setter function
void setter(byte value) {
if(value>0)
statusswitch=1;
else
statusswitch=0;
// send
Serial.println("send");
// for send data
digitalWrite(pin_direction_RX_TX, HIGH);
delay(5);
Serial0.print(address, DEC);
Serial0.print(" = ");
Serial0.println(statusswitch);
delay(5);
// for get data
digitalWrite(pin_direction_RX_TX, LOW);
}
Download this sketch
// demo sketch for Arduino UNO get RS485 data from Z-UNO
// add library SoftwareSerial
#include
// specify pins rx and tx respectively
SoftwareSerial mySerial(2, 3);
// pin for send/get rs485
int pin_direction_RX_TX = 10;
// pin led
int pinled = 8;
// value status led
int statusled = 0;
// to retrieve data from SoftwareSerial
String inputString0 = "";
// a sign of the end of the resulting string
boolean stringComplete0 = false;
// a sign of correct data
boolean res = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// SoftwareSerial begin
mySerial.begin(9600);
pinMode(pin_direction_RX_TX, OUTPUT);
// for get rs485 data
digitalWrite(pin_direction_RX_TX, LOW);
// led
pinMode(pinled,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(pinled,statusled);
// reserve 50 bytes for the inputString0:
inputString0.reserve(50);
}
void loop() {
serialEvent0();
if (stringComplete0) {
Serial.print(inputString0);
res = false;
// control a sign of correct data
if(inputString0.charAt(0) == '1' && inputString0.charAt(1) == '=') {
if(inputString0.charAt(2) == '0')
statusled=0;
else
statusled=1;
digitalWrite(pinled,statusled);
res=true;
}
// clear :
inputString0 = "";
stringComplete0 = false;
// send answer to rs485
Serial.println("send");
digitalWrite(pin_direction_RX_TX, HIGH);
delay(25);
if(res==true)
mySerial.println("ok");
else
mySerial.println("false");
delay(5);
digitalWrite(pin_direction_RX_TX, LOW);
}
}
// SerialEvent
void serialEvent0() {
if (mySerial.available() > 0) {
// get byte:
char inChar = (char)mySerial.read();
// add to string
inputString0 += inChar;
Serial.print(inChar);
// /n - end of transmission
if (inChar == '\n') {
stringComplete0 = true;
}
}
}
Download this sketch